|
Research programme
Corrosion protection In the field of corrosion protection our research is focused on the following topics:
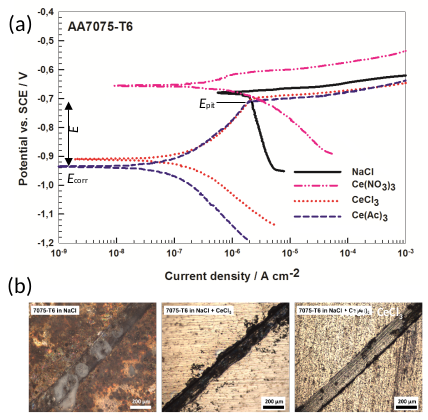
Conversion coatings Conversion coatings can be defined as coatings formed by conversion from soluble salt to a slightly soluble or insoluble oxide and/or hydroxide which precipitates either throughout the metal surface, or at intermetallic particles which are electrochemically more noble in respect to surrounding matrix and where oxygen reduction takes place. Inhibitory action of these conversion coatings is based on the retardation of cathode reaction (i.e. oxygen evolution) on corroding surfaces. Today three main types of conversion coatings are being explored on aluminium alloys: rare earth coatings, zirconium and/or titanium coatings and trivalent chromium coatings:
Conversion coatings: selected publications
Projects related to conversion coatings
|